Object representations
Overview
Different representation modes are available for the different objects inside the software. Some of these representation modes are always available and some are available only if the component contains the necessary information. A typical example is the Inspection representation which is only available for a cloud (or mesh) only if the cloud (or mesh) has been inspected.
Note about scalar representation modes
In these modes, the colors associated with the points are defined according to a gradient which can be edited by the user with the Edit Colors command.
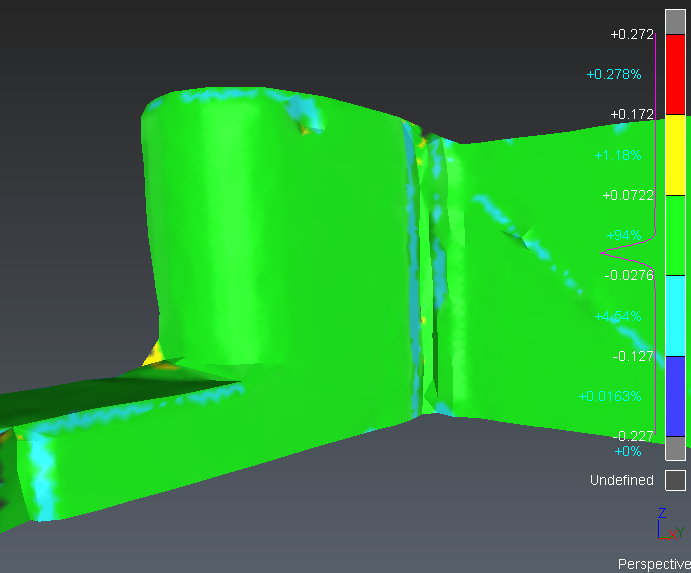
For some objects, it is important to understand the concept of the normal orientation to understand the representation. The normal of an object is the "outside" of this object. The “outside" is the side from where the object is scanned/viewed. At the opposite, the "inside" means inside the material itself. For instance, the orientation of meshes or surfaces is very important for inspection. In the software, meshes and surfaces have a color for the “inside” and another one for the “outside”, so it is very easy to detect when the normal is not correctly oriented. The “outside” color is also shinier than the “inside” color.
To change the transparency, select your object, then do a right click and select Transparency (not available on polylines), or use the representation icon in the tree.
More parameters are available in the command Settings. This command allows you to change more displayed parameters for each type of objects (clouds, meshes, polylines …). You can change default parameters (for all objects you will create or import), or current parameters (for the selected objects).
Cloud
|
Smooth |
Always available. |
|
|
Flat |
Always available. |
|
|
Smooth with back in reversed color |
Differentiate front and back colors of points, allowing to better distinguish inside and outside parts of the point cloud. Available if scanning position/directions are known. |
|
|
Real Color |
Available if RGB colors are known. |
|
|
Scalar attributes |
|
|
|
This representation displays a scalar value standing for the ratio of light received by the scanner. |
|
|
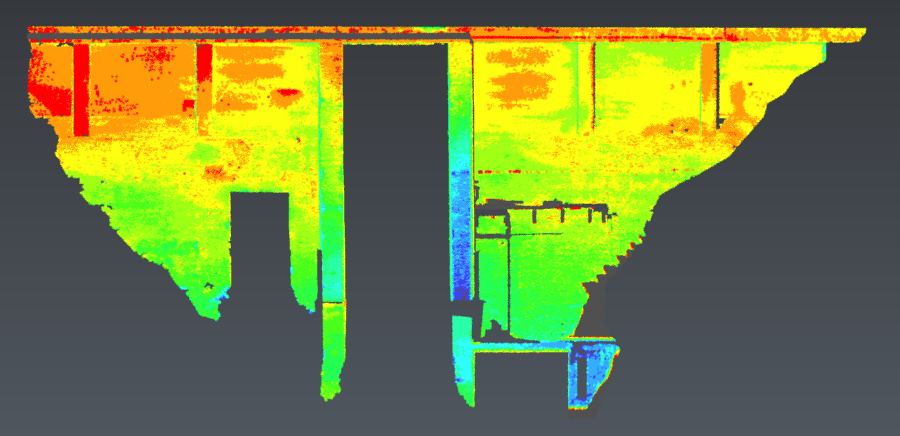
This representation displays a scalar value standing for the associated analysis (deviations, slope, elevation, etc.). Available if computed. |
|
|
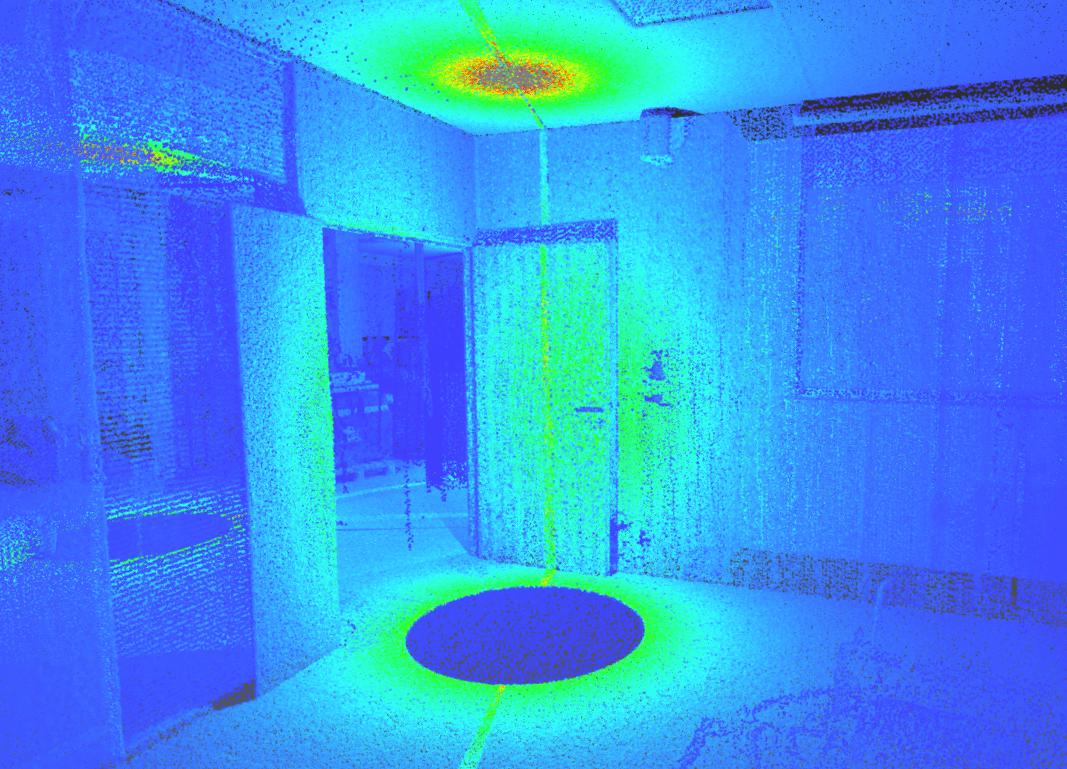
This representation displays a scalar value standing for the density around the point. Available if computed. |
|
|
This representation displays a scalar value: each point stores the time when it was recorded. |
|
|
Index attributes |
|
|
|
Available if classified points. |
|
|
It describes a combination of 2 values:
Available with compatible scanners. There are five possible values:
|
|
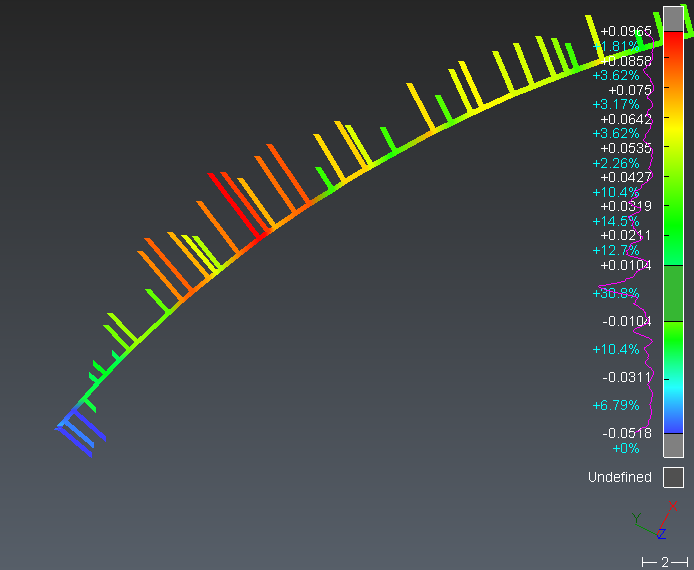
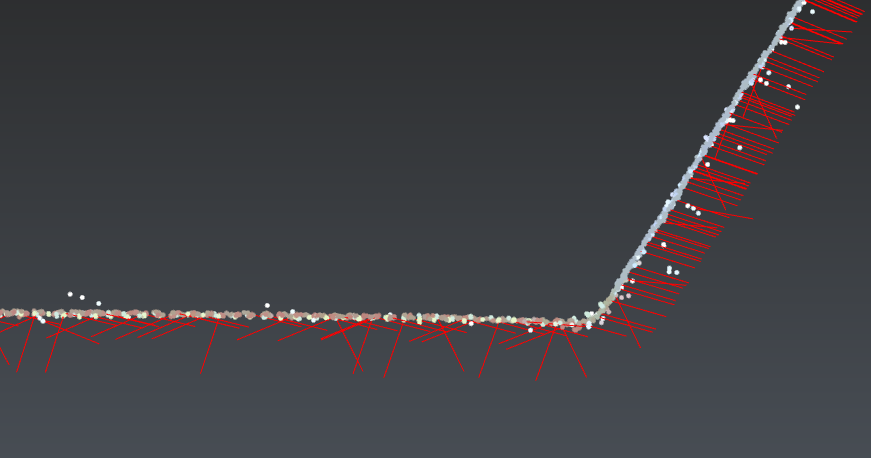
It is possible to display the scanner locations and/or scanning directions.
The scanner locations are displayed using red spheres. This is only available with static scans and when the setup positions are known. Note that red spheres can also display locations of images: refer to Image Navigation Toolbar.
The scanning directions are displayed using small red lines added to some points (from the measured point to the device). This is available on any point cloud when the scanning directions are known. It is suitable to see the beam incidence angle and is used to orient the estimated normal of the point. Scanning directions and normals are often confused: normals are perpendicular directions to a surface which is estimated when dealing about a point cloud (you can use Align to surface to see the normal of the hovered point). Note that wrong scanning directions will misorient normals which could lead to wrong mesh orientation (please read Exercise: Understand meshes orientation) or may affect the rendering (shading).
 Display of scanning directions
Display of scanning directions
Mesh
|
Smooth |
Always available |
|
|
Flat |
Always available |
|
|
Wire |
Always available |
|
|
Smooth + Wire |
Always available |
|
|
Flat + Wire |
Always available |
|
|
Textured |
Available if texture is defined (images applied to the triangles) |
|
|
Real Color |
Available if a RGB value (color) is associated with the vertices |
|
|
Inspection |
Available if an intensity or an inspection value is associated with the vertices |
|
|
Color per triangle |
Only available when the mesh comes from a BIM object. The color is associated with the triangles. |
|
Polyline/Set of polylines
|
Segments |
Always available |
|
|
Segments and vertices |
Always available |
|
|
Inspection |
Available if an inspection value is associated with the point |
|
You can also display the names of points, polylines, set of polylines in the scene by checking the option 'Show Text'.
CAD surface
|
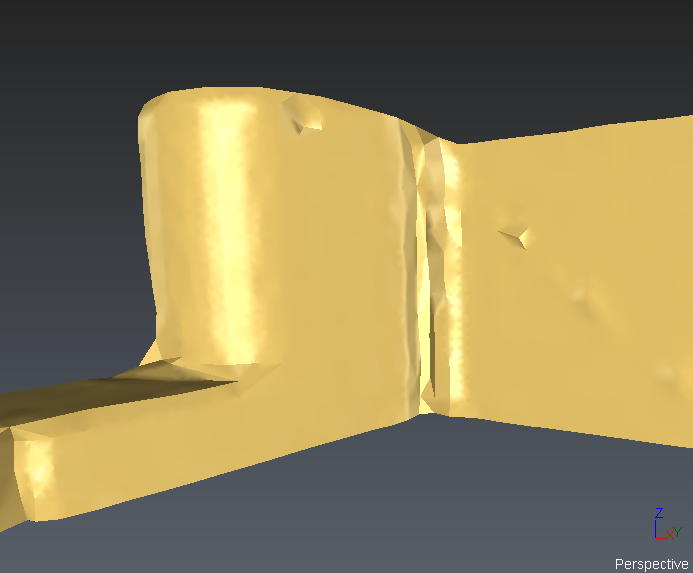
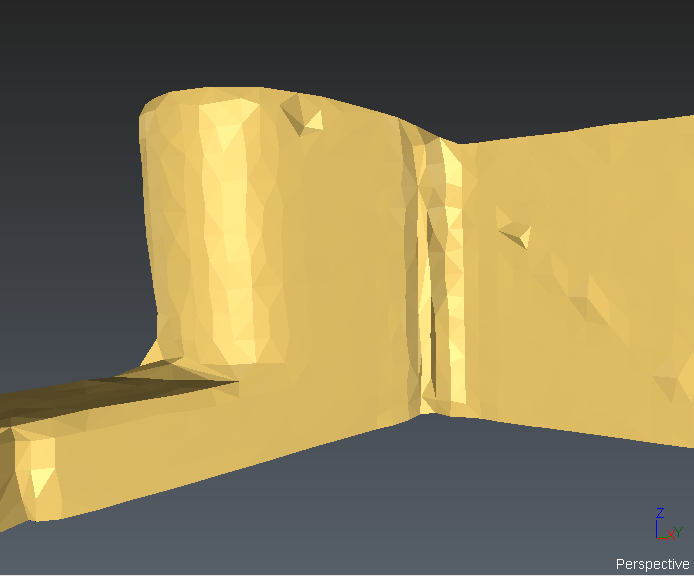
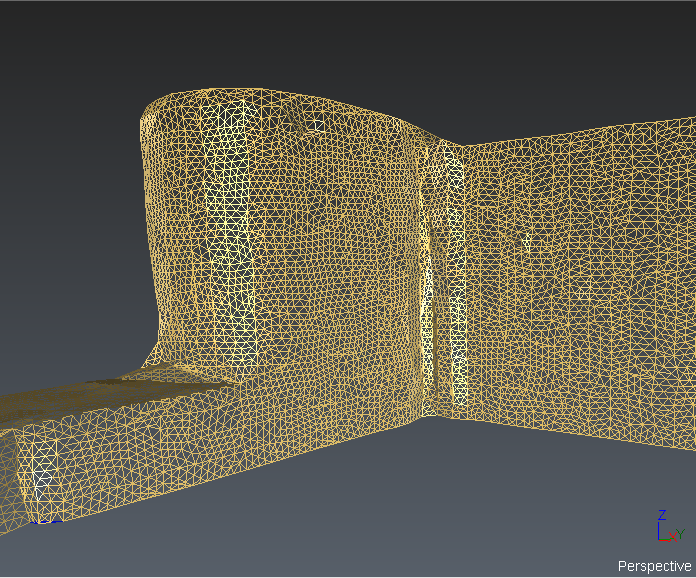
Smooth + Isometrics |
Always available Isometrics can be hidden. |
|
CAD Representation
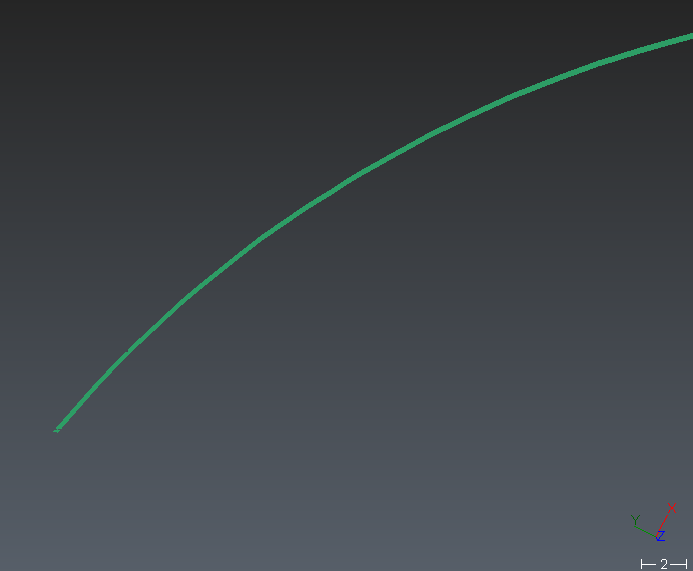
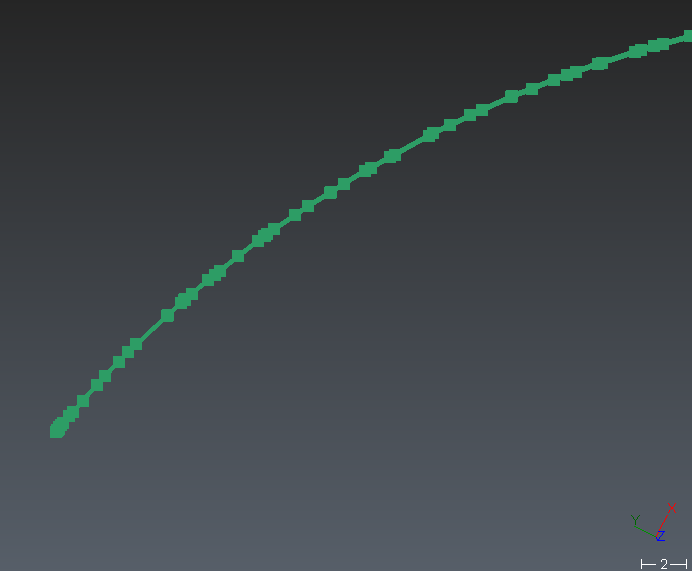
Sometimes, you may see that some CAD objects or polylines converted from CAD curves (AutoCAD) do not have a good aspect (not smooth enough, too much segmented). This is a side effect due to the technique used to represent a NURBS surface.
A NURBS surface cannot be displayed “as is”. It requires some transformation so that your graphic board can make the representation. This transformation is called “discretization” and consists in sampling the continuous surface or curve with “discrete” points.
In this process, the surface or curve is “simplified” with a certain error called “deflection”. By default, the software takes an adaptative deflection based on the dimension and the scale of the objects; but in some cases this value is not low enough to get a good representation. In such situation, it is possible to set the discretization independently thanks to Edit display discretization command which can be run on each object (directly from the treeview).
BIM Object
|
BIM |
Colors and transparency stored in .ifc or .rvt. Always available |
|
|
Flat |
Single editable color. Always available |
|